Leetcode 115. Distinct Subsequences
문제 개요
전체 문자열 string와 찾는 문자열 target가 주어진다. string의 문자를 순차적으로 조합하여 target를 완성할 수 있는 경우의 수를 구해야 한다.
예를 들어 , string = "rabbbit", t = "rabit"으로 주어졌을때, 결과 값은 아래의 과정으로 3이 나오게 된다.
rabbbit
rabbbit
rabbbit
모호한 부분
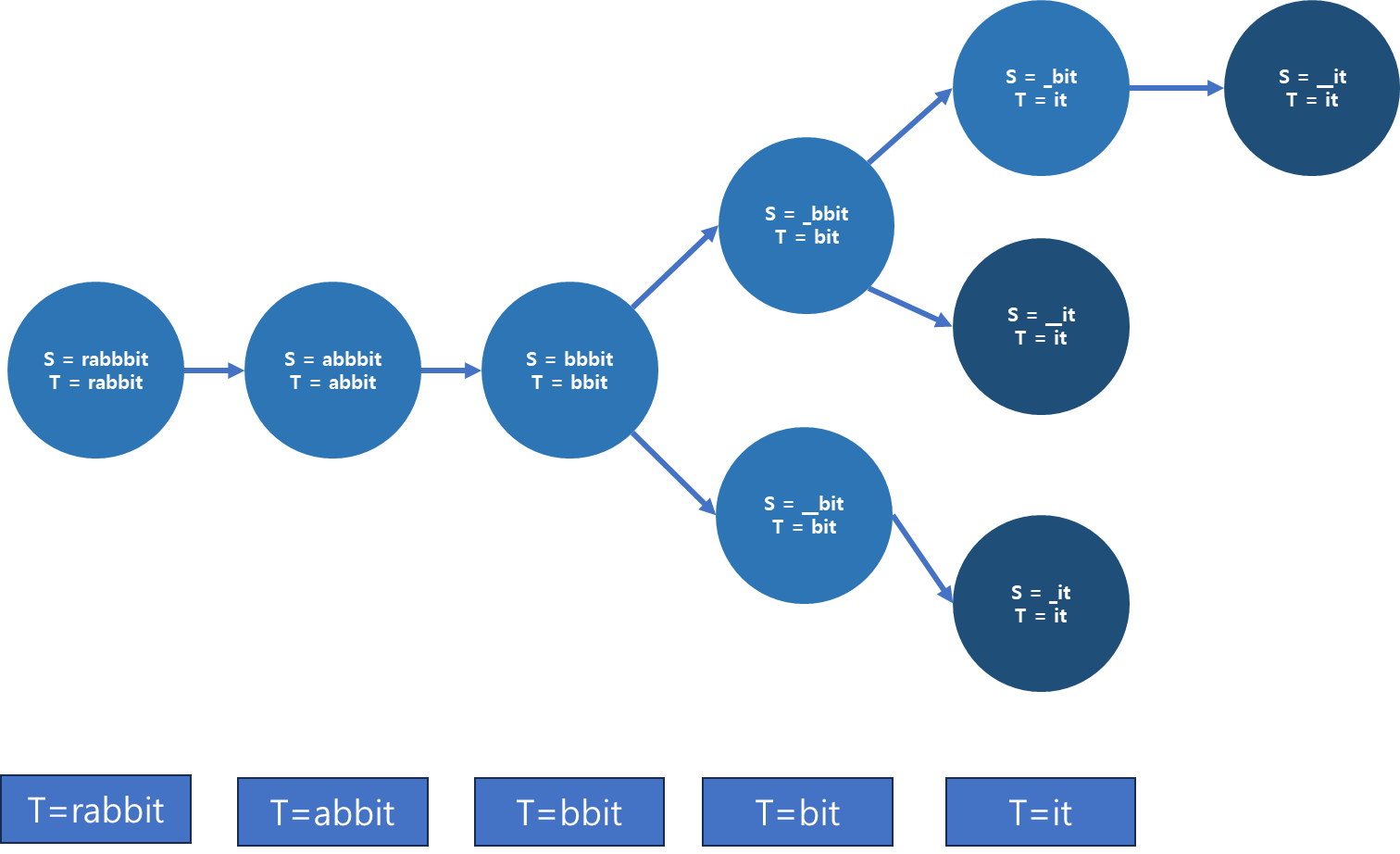
문자열 string을 순서대로 탐색하면서 target의 개수를 구해야 한다.string내에 문자를 선택하면 target의 문자도 아래의 그림처럼 줄어들지 않을까?
string = rabbbit, target = rabbit
string = bbit, target = bit // ra_bbit
string = bit, target = it // _bit
string = it, target = it // _it
string = it, target = it // b_it
string = bbit, target = bit // rab_bit
string = bit, target = it // _bit
string = it, target = it // _it
string = it, target = it // b_it
string = bbit, target = bit // rabb_it
string = bit, target = it // _bit
string = it, target = it // _it
string = it, target = it // b_it
이를 다시 그래프로 그려보면, 결과는 3이 나온다. string에 있는 문자를 바탕으로 target을 줄여나아가 분기가 될 만한 경우의 수가 3이기 때문이다.
이를 바탕으로, dfs와 cache 조합으로 작성한 코드는 다음과 같다.
class Solution:
def numDistinct(self, string: str, target: str):
cache = {} # 캐시 설정
def dfs(string, target):
if (string,target) in cache.keys():
return cache[(string,target)]
# target과 string이 동일하면 가지수는 1가지 이다.
if target == "" or string == target:
cache[(string,target)] = 1
return 1
# target을 기준으로 string의 문자들을 비교한다.
result = 0
for string_idx, string_char in enumerate(string):
if string_char == target[0]:
result += dfs(string[string_idx + 1:], target[1:])
cache[(string,target)] = result
return result
dfs(string, target)
return cache[(string, target)]
위의 알고리즘은 기본 테스트 케이스는 통과하지만, 제출 시 시간 초과가 났다. 시간 초과가 난 이유는 아래와 같이 분석된다.
1. 반복문 뒤에 재귀함수로 호출
아래의 반복문에서 for loop와 재귀함수를 돌면서 big-O가 len(string) ^ len(string + 1) ... 로 점점 늘어난다. 하지만 cache가 있어서 이미 해결한 문제는 반복문이 돌지 않을 것이다. 따라서 반복문 뒤에 재귀함수를 적용하는 건 시간복잡도 입장에서 적절해보이지 않는다.
for string_idx, string_char in enumerate(string):
if string_char == target[0]:
result += dfs(string[string_idx + 1:], target[1:])
2. 잦은 문자열 복사
재귀함수로 매개변수(parameter)를 넘길 때, 문자열 복사가 이루어진다. 따라서 공간 복잡도도 O(len(string) + len(string - 1) ...) = O(len(string) ^ 2)이고 복사를 하는 시간 복잡도도 O(len(string)^2)가 나온다. 복사가 어마어마하게 나오기 때문에 이 또한 적절해 보이지 않는다.
해결 전략
string의 문자 길이가 target 문자 길이보다 작을 경우 subsequence가 아니므로 경우의 수는 0이다.
target 문자가 빈 문자 경우 subsequence는 s의 문자가 빈 문자이다.
string과 target이 일치할 경우 경우의 수는 1이다.
string과 target이 일치하는지 확인하기 위한 방법은 아래와 같다.
1. string과 target의 첫 문자를 비교한다.
2. string과 target의 첫 문자가 같으면 둘의 다음 문자를 바교한다.
3. string과 target의 첫 문자가 다르면 string의 다음 문자를 비교한다.
따라서 아래와 같은 tree가 만들어지며, 이를 통해 distinct subsequence를 구할 수 있다.
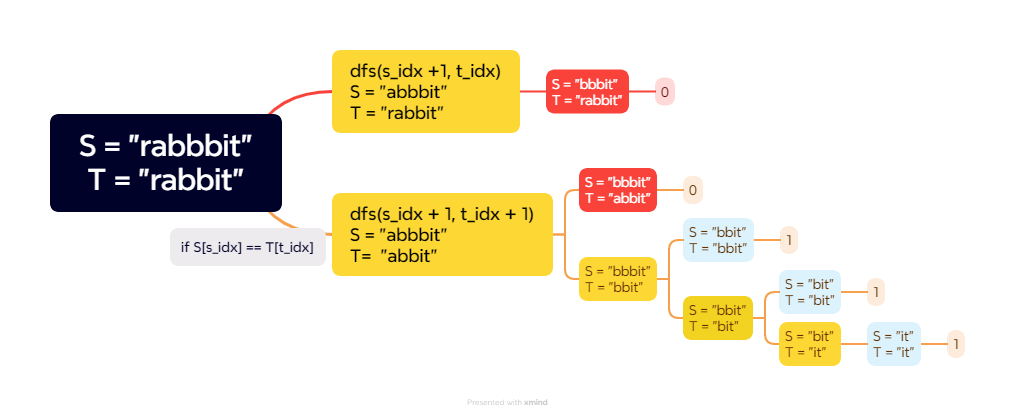
위의 내용을 바탕으로 코드를 작성하면 다음과 같다.
def numDistinct(self, string: str, target: str):
cache = [ [-1] * 1001 for _ in range(1001)]
def dfs(string, target, string_idx, target_idx):
if target_idx >= len(target):
return 1
# string문자 길이가 target의 문자길이보다 작은 경우
if len(string) - string_idx < len(target) - target_idx:
return 0
# cache가 존재하는 경우 cache 반환
if cache[string_idx][target_idx] != -1:
return cache[string_idx][target_idx]
# 안맞는 경우
result = dfs(string, target, string_idx + 1, target_idx)
# 맞는 경우
if string[string_idx] == target[target_idx]:
result += dfs(string, target, string_idx + 1, target_idx + 1)
# 결과 계산
cache[string_idx][target_idx] = result
return cache[string_idx][target_idx]
return dfs(string, target, 0, 0)
회고
재귀 함수를 작성할 때는 재귀함수 또한 반복문임을 기억해야 한다. 코드가 재귀 함수와 반복문을 같이 존재하고 있으면 다시 한 번 생각하면 좋겠다.
문제를 해결하려 할 때, 가능한 경우만 생각하고 있는데, 가능하지 않을 때 어떻게 접근해야 하는지도 생각해야 할 필요가 있다.
데이터를 계산하기 위해 복사하곤 하는데, 이를 최소화 하는 방법을 생각하자.